Ensuring Robust OT Cybersecurity: The Crucial Role of Auditing and Compliance
In today’s interconnected world, Operational Technology (OT) systems have become the backbone of critical infrastructure industries such as energy, manufacturing, and healthcare. While the convergence of IT (Information Technology) and OT has brought numerous benefits, it has also opened these systems to new and evolving cybersecurity threats. To mitigate these risks, organizations must implement comprehensive OT cybersecurity measures. Among these measures, regular security audits and compliance with industry standards and regulations stand out as essential components.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of auditing and compliance in the realm of OT cybersecurity.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Security audits and assessments play a pivotal role in ensuring the robustness of OT cybersecurity. Here are some key reasons why they are indispensable:
Identifying Vulnerabilities: Regular audits help in identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in OT systems. By proactively finding these issues, organizations can take timely corrective actions to prevent potential breaches or system failures.
Risk Management: Audits provide a structured approach to risk management. They allow organizations to prioritize their cybersecurity efforts based on identified risks, ensuring that critical assets and processes are adequately protected.
Compliance Validation: Many industry regulations and standards mandate regular security audits. By conducting these audits, organizations not only comply with legal requirements but also demonstrate their commitment to cybersecurity to stakeholders and regulatory bodies.
Continuous Improvement: Audits are not just about finding problems; they are also about continuous improvement. They help organizations fine-tune their cybersecurity strategies and adapt to evolving threats and technologies.
Incident Response Preparedness: Audits can uncover weaknesses in incident response plans and procedures. Addressing these gaps ensures that organizations are better prepared to respond effectively to cyber incidents when they occur.
Complying with Industry Standards and Regulations
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is another critical aspect of OT cybersecurity. Here’s why it matters:
Legal Requirements: Various industries have established regulations that mandate specific cybersecurity measures to protect critical infrastructure and sensitive data. Non-compliance can result in legal consequences, fines, and damage to an organization’s reputation.
Best Practices: Industry standards, such as the IEC/ISA 62443 Cybersecurity Framework, provide a blueprint for effective cybersecurity. Complying with these standards helps organizations implement best practices and stay ahead of emerging threats.
Interoperability and Compatibility: Adhering to industry standards ensures interoperability and compatibility with other systems and organizations. This is particularly important for OT systems, which often rely on diverse technologies and vendors.
Customer Trust: Compliance with cybersecurity standards can enhance an organization’s reputation and build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders. It demonstrates a commitment to security and reliability.
Risk Mitigation: Regulations and standards are designed to mitigate specific risks associated with OT cybersecurity. Following these guidelines helps organizations reduce their vulnerability to cyber threats.
Auditing and Compliance from an IEC/ISA 62443 Standard Perspective
One key framework that plays a pivotal role in achieving this is the ISA 62443 standard, also known as the “Industrial Automation and Control Systems Security” standard. This comprehensive set of guidelines is designed to help organizations in industrial sectors establish robust cybersecurity measures.
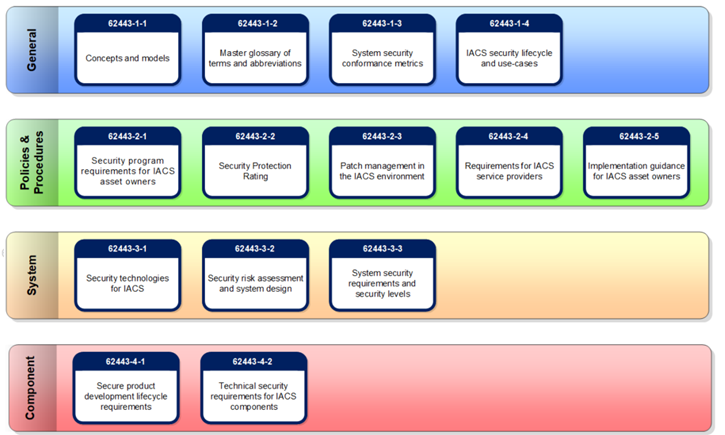
Auditing and compliance are central components of the IEC/ISA 62443 standard. Here’s how they fit into the framework:
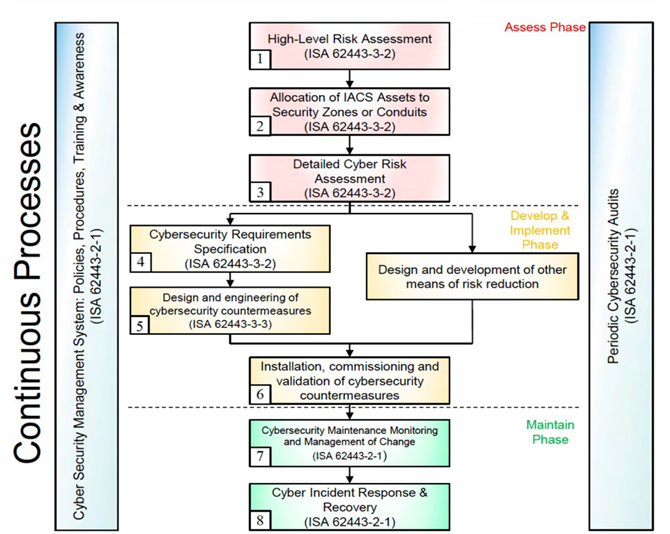
Risk Assessment: IEC/ISA 62443-3-2 emphasizes the importance of conducting thorough risk assessments. Auditing plays a crucial role in this process by identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the IACS. Compliance, on the other hand, ensures that the identified risks are addressed in accordance with the standard’s recommendations.
Risk Reduction: Regular auditing and compliance activities help identify and mitigate vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of cyberattacks that could disrupt critical industrial processes.
Security Policies: IEC/ISA 62443-2 encourages organizations to develop and implement robust security policies tailored to their specific needs. Compliance ensures that these policies are followed and regularly audited to verify their effectiveness.
Network Security: IEC/ISA 62443 provides guidelines for establishing secure network architectures. Compliance with these guidelines is critical to safeguarding industrial networks. Regular audits help verify that the network configurations adhere to these standards and are secure against emerging threats.
Incident Response: In the event of a cybersecurity incident, an efficient and well-defined incident response plan is essential. Compliance with IEC/ISA 62443 helps organizations establish effective response procedures, while audits can test the readiness and effectiveness of these plans.
Continuous Improvement: Auditing provides valuable insights that can be used to refine and improve cybersecurity measures over time. Compliance ensures that these improvements are consistently implemented.
Resilience: By following IEC/ISA 62443 and conducting audits, organizations enhance their resilience against cyber threats, ensuring the continued operation of critical infrastructure.
Lifecycle Management: The standard emphasizes a lifecycle approach to IACS cybersecurity. Compliance ensures that cybersecurity measures are integrated into every phase of the system’s lifecycle, from design and implementation to operation and maintenance. Auditing verifies that these measures are consistently applied.
Conclusion
Auditing and compliance are indispensable pillars of a robust OT cybersecurity strategy. They help organizations identify vulnerabilities, manage risks, and demonstrate their commitment to security. By conducting regular security audits and complying with industry standards and regulations, businesses can safeguard their critical infrastructure, protect sensitive data, and ensure the continued operation of their OT systems.
In the realm of industrial cybersecurity, the IEC/ISA 62443 standard is a beacon of guidance. Auditing and compliance as integral components of this framework. They enable organizations to proactively address vulnerabilities, reduce risks, and ensure the reliability and safety of their operations. By adhering to IEC/ISA 62443 and embracing auditing and compliance practices, industrial sectors can fortify their defenses against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, ultimately contributing to a safer and more secure industrial ecosystem.
